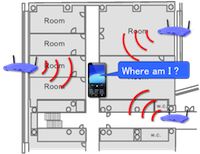
Recently Wi-Fi positioning systems are gaining popularity in pervasive computing and machine learning community. However, collecting a sufficient amount of calibration data is rather tedious and time consuming, especially indoor scenarios where GPS coverage is unavailable. To alleviate this problem, we present a semi-supervised learning from “route-annotated data”, where a human walks to collect radio signal strength (RSS) values while route information is annotated independently. The basic idea is to allocate temporary location information to each RSS values by using route information as dynamic programming, thereby many conventional machine learning methods become adaptable. Experimental results with real-world deployment demonstrate the practical utility of the method.