Driving behavior modeling (DBM) is widely used in the intelligent vehicle field to prevent accidents, which predicts actions that vehicles should take to optimize safe driving behaviors. According to some statistics, accidents easily happen at un-signalized intersections, modeling driving behavior at such places is of great importance.
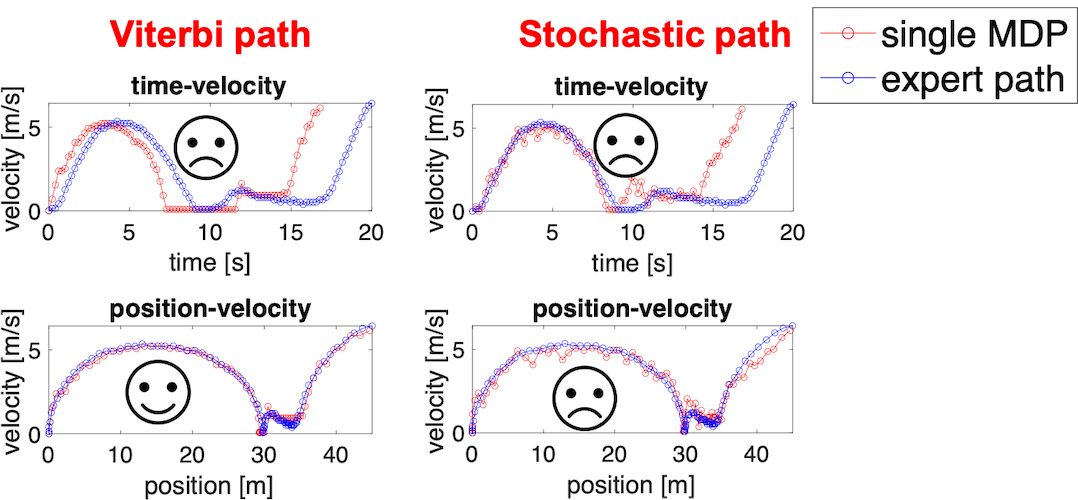
Inverse reinforcement learning is gaining popularity in recent DBM tasks, which learns the reward functions of reinforcement learning from real driving data. However, current inverse reinforcement learning-based DBM methods fail to predict proper behaviors at the un-signalized intersections in the aspects of smoothness and stopping behavior by just using a single Markov decision process (MDP). When modeling driving behavior at the intersection, there are two problems with the single-MDP method. If planning behavior by maximizing the reward, the car tends to stop around the stop line for a long time to earn as much reward as possible. While by stochastic policy from reward expectations, stopping time around the stop line becomes shorter but unusual acceleration will happen. In other words, it is difficult for current methods to maintain a balance between the stability of the speed and the rationality of the stopping behavior at the stop line. That is abnormal for real human driving behavior.
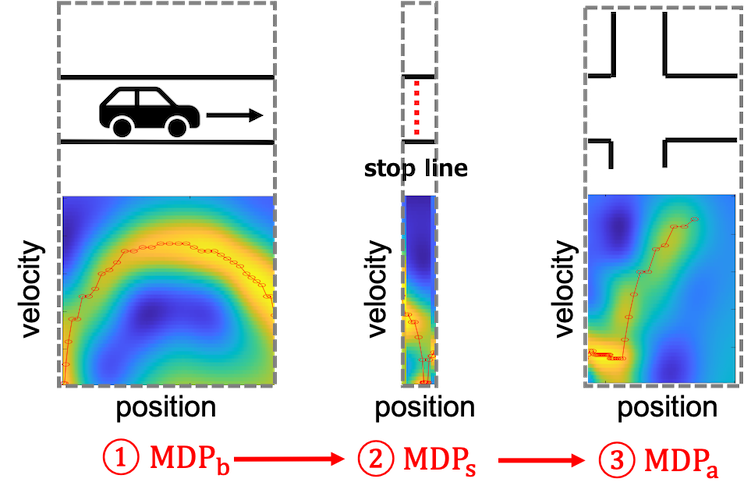
In this project, for smoothening the driving path, we divide the target intersection into three parts according to the position of the stop line. A sequential MDPs structure is proposed to model the driving behavior at the intersection separately. And a Poisson model is used to simulate the stopping behavior around the stop line close to human driving behavior. The experimental results show that our model generates a smoothed driving path with reasonable stopping behavior at the un-signalized intersection.
Publications
Shaoyu Yang, Hiroshi Yoshitake, Motoki Shino, Masamichi Shimosaka.
Smooth and Stopping Interval Aware Driving Behavior Prediction at Un-Signalized Intersection with Inverse Reinforcement Learning on Sequential MDPs.
The 2021 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV21)
Smooth and Stopping Interval Aware Driving Behavior Prediction at Un-Signalized Intersection with Inverse Reinforcement Learning on Sequential MDPs.
The 2021 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV21)